Call Us - 0458 190 172
Pigmentation

Common Skin Concern
Pigmentation
Pigmentation refers to the colour of our skin, which is determined by the quantity of melanocytes (cells that produce pigment). These cells produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin colour. When melanin production is excessive or abnormal, it can lead to areas of hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation occurs when there is an excess of melanin, resulting in patches of skin that are darker than the surrounding area. Hypopigmentation happens when there is a loss of skin pigment, causing lighter patches compared to the rest of the skin.
Schedule Your Treatment Today!

Common Skin Concern
Pigmentation
Pigmentation refers to the colour of our skin, which is determined by the quantity of melanocytes (cells that produce pigment). These cells produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin colour. When melanin production is excessive or abnormal, it can lead to areas of hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation occurs when there is an excess of melanin, resulting in patches of skin that are darker than the surrounding area. Hypopigmentation happens when there is a loss of skin pigment, causing lighter patches compared to the rest of the skin.
Schedule Your Treatment Today!
What Causes Skin Pigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation occurs when there is an overproduction of melanin, which can have various causes. Identifying the specific cause of your hyperpigmentation is essential for effective treatment. Common causes include.
- Ageing
- Trauma
- UV Radiation Exposure
- Medications
- Hormonal Changes
- Genetic Predisposition


What Causes Skin Pigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation occurs when there is an overproduction of melanin, which can have various causes. Identifying the specific cause of your hyperpigmentation is essential for effective treatment. Common causes include.
- Ageing
- Trauma
- UV Radiation Exposure
- Medications
- Hormonnal Changes
- Genetic Predispostion
Types of Pigmentation
Types of Pigmentation
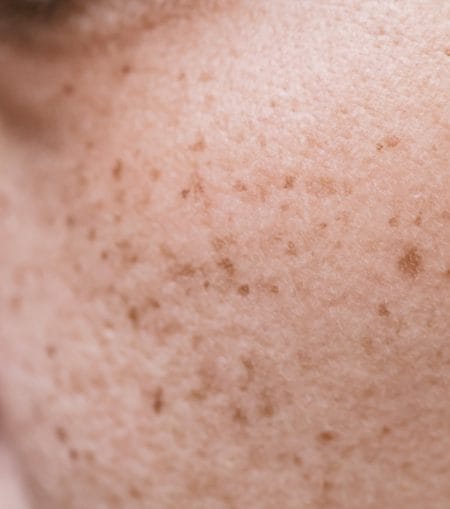
Freckles
Freckles are small spots of concentrated melanin that can vary in colour, including brown, tan, red, black, or yellow. They form when the skin is exposed to UVB radiation from the sun, which activates melanocytes and increases melanin production.
Freckles can appear anywhere on the body but are often found on the face, arms, neck, back, and chest. Usually, they are harmless and tend to fade with less sun exposure.

Freckles
Freckles are small spots of concentrated melanin that can vary in colour, including brown, tan, red, black, or yellow. They form when the skin is exposed to UVB radiation from the sun, which activates melanocytes and increases melanin production.
Freckles can appear anywhere on the body but are often found on the face, arms, neck, back, and chest. Usually, they are harmless and tend to fade with less sun exposure.
Age Spots
Age spots, also known as solar lentigines, are well-defined areas of pigmentation that are darker and more pronounced. Unlike freckles, age spots are scattered and tend to develop later in life, which is why they are often called age spots. They are caused by prolonged sun exposure, resulting in excess melanin production and abnormal pigment retention.


Age Spots
Age spots, also known as solar lentigines, are well-defined areas of pigmentation that are darker and more pronounced. Unlike freckles, age spots are scattered and tend to develop later in life, which is why they are often called age spots. They are caused by prolonged sun exposure, resulting in excess melanin production and abnormal pigment retention.
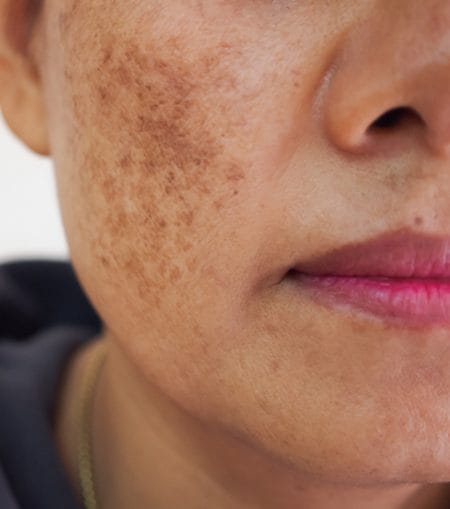
Melasma
Melasma is a skin condition characterised by symmetrical, dark, irregular patches of pigmentation on the cheeks, nose, upper lip, chin, and forehead. It is common in women, particularly during pregnancy or when there is a hormonal imbalance. Although it can affect all skin types, it is more prevalent in those with darker Fitzpatrick skin types.
Melasma occurs when melanocyte cells are stimulated by estrogen and progesterone, leading the skin to produce an excess of melanin and are also known as lentigines, or liver spots, typically appearing on the back of the hands and face. They are flat, light brown patches that do not cause itching or scaling.

Melasma
Melasma is a skin condition characterised by symmetrical, dark, irregular patches of pigmentation on the cheeks, nose, upper lip, chin, and forehead. It is common in women, particularly during pregnancy or when there is a hormonal imbalance. Although it can affect all skin types, it is more prevalent in those with darker Fitzpatrick skin types.
Melasma occurs when melanocyte cells are stimulated by estrogen and progesterone, leading the skin to produce an excess of melanin.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is a form of hyperpigmentation that arises after skin inflammation or injury. PIH is frequently associated with acne, trauma, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
Severe inflammation or trauma can disrupt the lower layer of the epidermis, prompting melanocytes to produce melanin that can seep into and become trapped in the deeper layers of the skin. This leads to deeper pigmentation that can be more challenging to treat.
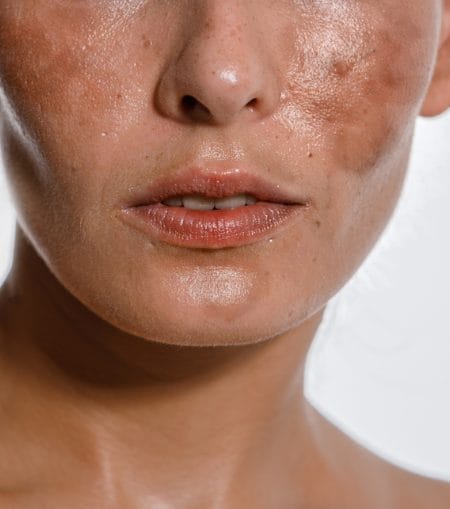


Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is a form of hyperpigmentation that arises after skin inflammation or injury. PIH is frequently associated with acne, trauma, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
Severe inflammation or trauma can disrupt the lower layer of the epidermis, prompting melanocytes to produce melanin that can seep into and become trapped in the deeper layers of the skin. This leads to deeper pigmentation that can be more challenging to treat.
Our Treatments for Pigmentation
At Laser Skin Aesthetics, we provide a range of treatments to address pigmentation issues, whether they're due to sun exposure, aging, or hormonal changes. Our variety of treatments and skincare products may help improve your skin.
If you’re uncertain about which treatment is best for you, schedule a free skin consultation with us, and we'll customize a treatment plan based on your skin needs and goals.
Our Treatments for Pigmentation
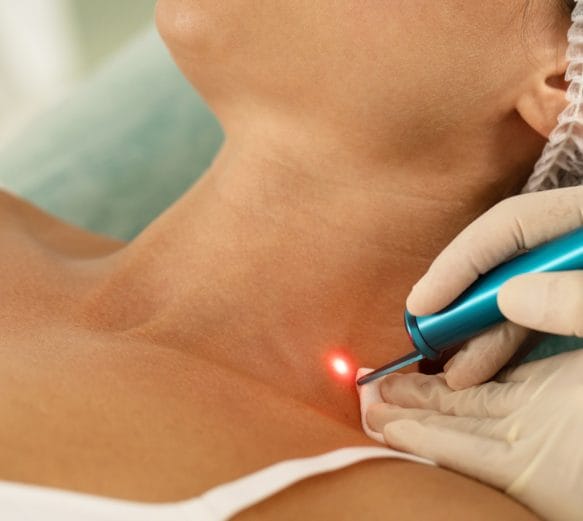
Laser Pigmentation Removal
This procedure works by emitting high-intensity light energy in the form of a laser beam which directly works to effectively remove sunspots, fragments, brown pigmentation and hyper pigmentation without damanging the surrounding tissue.
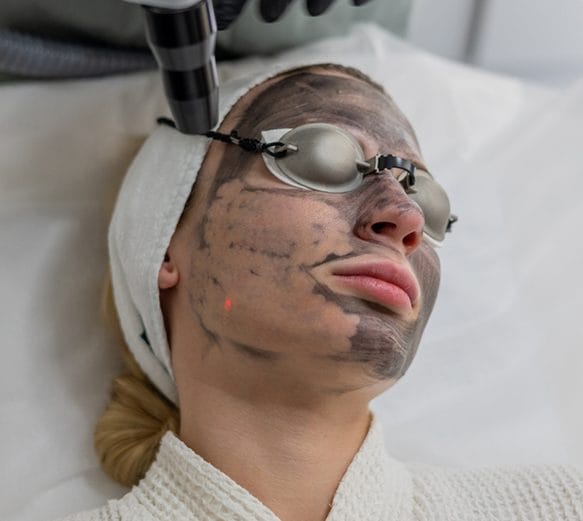
Laser Carbon Peel
This includes a carbon-based mask to absorb impurities and excess oil followed by laser activation to remove carbon particles and pigmentation. The heat from the laser stimulates collagen production, promoting skin renewal.
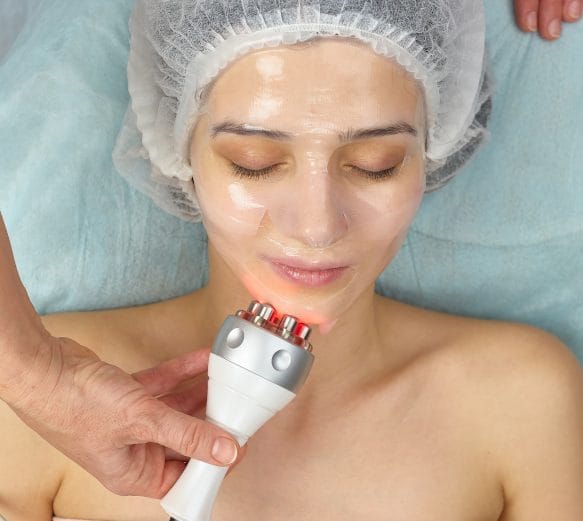

RF Skin Tightening
RF skin tightening combines radio frequency and laser rejuvenation to induce a powerful, natural healing response in your skin. This procedure targets fine lines, wrinkles, loose skin, scarring, stretch marks and enlarged pores.
Laser Skin Whitening
A non-invasive resurfacing procedure that exfoliates the uppermost layers of the skin to gently removes dead skin cells and skin debris. It also stimulates cell renewal, detoxification, and the synthesis of collagen and elastin.

Laser Pigmentation Removal
This procedure works by emitting high-intensity light energy in the form of a laser beam which directly works to effectively remove sunspots, fragments, brown pigmentation and hyper pigmentation without damanging the surrounding tissue.

Laser Carbon Peel
This includes a carbon-based mask to absorb impurities and excess oil followed by laser activation to remove carbon particles and pigmentation. The heat from the laser stimulates collagen production, promoting skin renewal.

RF Skin Tightening
RF skin tightening combines radio frequency and laser rejuvenation to induce a powerful, natural healing response in your skin. This procedure targets fine lines, wrinkles, loose skin, scarring, stretch marks and enlarged pores.

Laser Skin Whitening
Designed to lighten dark spots, reduce hyperpigmentation, and enhance your skin’s natural radiance. This treatment breaks down excess melanin for a more uniform skin tone, followed by skin brightening which stimulates cell regeneration.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I prevent skin pigmentation?
You can prevent skin pigmentation by practising sun protection, such as wearing sunscreen daily, avoiding prolonged sun exposure, wearing protective clothing, and using hats and sunglasses. Additionally, avoiding harsh skin treatments and being cautious with certain medications can help prevent pigmentation issues.
Can skin pigmentation be reversed?
In many cases, yes, skin pigmentation can be improved or reversed with appropriate treatment. However, the effectiveness of treatment can vary depending on factors such as the underlying cause, the type of pigmentation, and individual skin characteristics. Consistent and proper treatment, along with preventive measures, can help manage and reduce skin pigmentation.
Is skin pigmentation harmful to my health?
While skin pigmentation itself is not harmful to health, certain conditions that cause pigmentation changes may be associated with underlying health issues. For example, sudden changes in pigmentation or the appearance of new or irregularly shaped moles should be evaluated by a dermatologist to rule out skin cancer or other serious conditions.
Can diet affect skin pigmentation?
There is some evidence to suggest that certain dietary factors, such as antioxidants and vitamins, can support overall skin health and potentially help manage pigmentation issues. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, and staying hydrated can contribute to maintaining healthy skin.
Can skin pigmentation be hereditary?
Yes, certain types of skin pigmentation, such as freckles, birthmarks, and some forms of hyperpigmentation, can have a hereditary component. Individuals with a family history of certain pigmentation issues may be more prone to developing them themselves.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I prevent skin pigmentation?
You can prevent skin pigmentation by practising sun protection, such as wearing sunscreen daily, avoiding prolonged sun exposure, wearing protective clothing, and using hats and sunglasses. Additionally, avoiding harsh skin treatments and being cautious with certain medications can help prevent pigmentation issues.
Can skin pigmentation be reversed?
In many cases, yes, skin pigmentation can be improved or reversed with appropriate treatment. However, the effectiveness of treatment can vary depending on factors such as the underlying cause, the type of pigmentation, and individual skin characteristics. Consistent and proper treatment, along with preventive measures, can help manage and reduce skin pigmentation.
Is skin pigmentation harmful to my health?
While skin pigmentation itself is not harmful to health, certain conditions that cause pigmentation changes may be associated with underlying health issues. For example, sudden changes in pigmentation or the appearance of new or irregularly shaped moles should be evaluated by a dermatologist to rule out skin cancer or other serious conditions.
Can diet affect skin pigmentation?
There is some evidence to suggest that certain dietary factors, such as antioxidants and vitamins, can support overall skin health and potentially help manage pigmentation issues. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, and staying hydrated can contribute to maintaining healthy skin.
Can skin pigmentation be hereditary?
Yes, certain types of skin pigmentation, such as freckles, birthmarks, and some forms of hyperpigmentation, can have a hereditary component. Individuals with a family history of certain pigmentation issues may be more prone to developing them themselves.
